Table of Contents
1. Steroid-Induced Acne
Steroids can cause acne breakouts due to their impact on hormone levels.
The increased production of sebum, a natural oil that lubricates the skin, can lead to clogged pores and the development of acne.
This side effect is more common in individuals who are already prone to acne.
How to manage steroid-induced acne:
– Keep the affected areas clean and dry
– Use non-comedogenic skincare products
– Avoid picking or squeezing acne lesions
– Consult a dermatologist for appropriate treatment options
– Maintain a healthy diet and lifestyle
2. Cardiovascular Complications
Steroids can have detrimental effects on the cardiovascular system, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
They can raise blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and triglycerides, leading to the development of atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries).
How to minimize cardiovascular complications:
– Regularly monitor blood pressure and cholesterol levels
– Engage in regular exercise
– Follow a heart-healthy diet
– Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
– Discuss any concerns with a healthcare professional
3. Liver Damage
Prolonged use of steroids can put strain on the liver, leading to liver damage or dysfunction.
Steroids are metabolized by the liver, and excessive use can overwhelm its detoxification capabilities, causing inflammation and potential long-term damage.
How to protect the liver:
– Limit alcohol consumption
– Avoid the use of other hepatotoxic substances
– Follow a balanced diet
– Consider liver support supplements, under medical guidance
– Regularly monitor liver function through blood tests
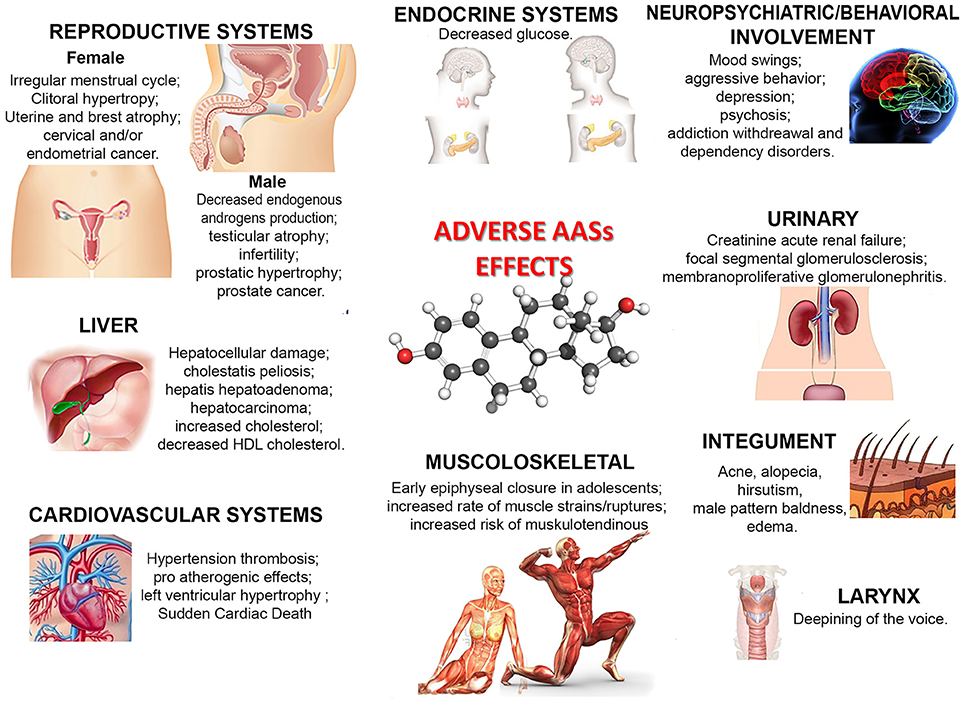
4. Hormonal Imbalances
Steroids can disrupt the body’s natural hormone production, leading to hormonal imbalances.
This can result in a range of side effects, including decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, irregular menstrual cycles, and infertility.
How to manage hormonal imbalances:
– Consult an endocrinologist for hormone replacement therapy, if necessary
– Maintain a healthy lifestyle and diet
– Engage in regular exercise
– Manage stress levels
– Discuss any concerns with a healthcare professional

5. Mood and Behavioral Changes
Steroids can affect mood and behavior, leading to mood swings, irritability, aggression, and even psychiatric disorders such as depression and anxiety.
These changes are thought to be related to alterations in neurotransmitter levels in the brain.
How to manage mood and behavioral changes:
– Seek support from mental health professionals
– Engage in stress-reducing activities
– Practice relaxation techniques
– Maintain a healthy lifestyle
– Communicate openly with loved ones about any changes experienced

6. Osteoporosis
Long-term steroid use can weaken bones and increase the risk of osteoporosis, a condition characterized by reduced bone density and increased susceptibility to fractures.
Steroids interfere with the normal process of bone remodeling, leading to bone loss.
How to prevent osteoporosis:
– Ensure an adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D
– Engage in weight-bearing exercises
– Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
– Discuss the use of bone-strengthening medications with a healthcare professional
– Regularly monitor bone density through bone mineral density tests
7. Eye Problems
Steroids can cause various eye problems, including cataracts and glaucoma.
Prolonged use of steroids can increase the risk of developing these conditions, which can lead to vision impairment or even blindness if left untreated.
How to protect eye health:
– Have regular eye exams
– Discuss the use of steroid-sparing medications with a healthcare professional
– Wear sunglasses to protect the eyes from UV radiation
– Follow proper contact lens hygiene
– Seek immediate medical attention for any changes in vision
8. Immune System Suppression
Steroids suppress the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections and delaying wound healing.
Prolonged use of steroids can weaken the body’s natural defense mechanisms, increasing the risk of infections.
How to support the immune system:
– Practice good hygiene, including regular handwashing
– Avoid close contact with individuals who are sick
– Stay up to date with vaccinations
– Eat a balanced diet rich in immune-boosting nutrients
– Discuss any concerns with a healthcare professional
9. Growth and Development Issues
Steroids can interfere with normal growth and development, particularly in adolescents.
Prolonged use of steroids can lead to stunted growth, delayed puberty, and compromised bone development.
How to support healthy growth and development:
– Monitor growth and development regularly
– Ensure a balanced diet with adequate nutrients
– Encourage regular exercise
– Discuss any concerns with a pediatrician or endocrinologist
– Follow a healthcare professional’s guidance on steroid use in adolescents

10. Increased Risk of Cancer
There is evidence to suggest that long-term steroid use may increase the risk of certain types of cancer, including liver, prostate, and breast cancer.
Steroids can promote the growth of cancer cells and interfere with the body’s natural defense mechanisms against cancer.
How to reduce the risk of cancer:
– Follow a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise
– Avoid exposure to known carcinogens
– Engage in regular cancer screenings
– Discuss any concerns with a healthcare professional
– Follow recommended guidelines for steroid use
In conclusion, while steroids can be beneficial in certain medical conditions, their long-term use can lead to various side effects. It is important to weigh the potential benefits against the risks and to use steroids under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Regular monitoring and open communication with healthcare providers can help minimize the risk of long-term side effects.